Cryptocurrency
How blockchain tech and dMRV can help carbon trading markets

There is a global consensus that greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are warming the planet, but efforts to accurately measure, report and verify these emissions continue to challenge researchers, nonprofits, corporations and governments.
This is especially the case with “nature-based” projects to reduce carbon dioxide levels, like planting trees or restoring mangrove forests.
This has inhibited the development of a voluntary carbon market (VCM) on which carbon offset credits are traded. These “offsets” are sometimes viewed as licenses to pollute, but VCMs overall are thought to be beneficial to the planet because they help quantify the environmental impact of industrial and consumer activities and, at least indirectly, motivate companies to curb emissions.
However, VCMs have recently come under intense criticism. A nine-month investigation by the United Kingdom’s Guardian newspaper and several other organizations found that more than 90% of “rainforest offset credits” approved by the leading certification firm Verra “are likely to be ‘phantom credits’ and do not represent genuine carbon reductions.”
This finding shook the carbon trading sector, but it has also spurred some new thinking about ways to measure, report or verify the efficacy of carbon-reduction projects. Digital monitoring, reporting and verification (dMRV), for example, largely automates this process, making use of new technologies like remote sensing, satellite imagery and machine learning. DMRV also uses blockchain technology for traceability, security, transparency and other purposes.
All this is still new, but many believe dMRV can reinvigorate carbon markets following the Verra scandal. It can also compensate for a shortfall of human auditors and inspectors available globally to assess GHG projects, especially the more problematic “nature-based” projects. In addition, it can gather a broader range of data and potentially make it available in real time. Importantly, it will allow a global comparison of projects for the first time.
“A huge difference”
“DMRV will make a huge difference here, since it moves the quantitative comparison of various nature-based interventions onto a global field where they can be comparable with each other — something that is not possible in the current systems as projects self-report against their own baselines,” Anil Madhavapeddy, a professor at the University of Cambridge and director of the Cambridge Centre for Carbon Credits, told Cointelegraph.
Some go even further. “Digital Measurement, Reporting, and Verification (dMRV) technology has the potential to revolutionize the way the voluntary carbon market (VCM) operates,” declared dClimate, a decentralized infrastructure network for climate data, in a March blog post.
Still, questions remain: Maybe this is all too little, too late for averting climate change? And if not too late, won’t progress stall if better methodologies aren’t developed, like quantifying how much a Brazilian rainforest reduces global carbon? Are blockchains necessary for the process, and if so, why? And can dMRV really “revolutionize” voluntary carbon markets, or is this just excessive hyperbole?
“It is not too late,” Miles Austin, CEO of climate tech firm Hyphen Global AG, told Cointelegraph. “We find ourselves at a pivotal moment.” The Verra scandal and continued allegations of “greenwashing” on the part of corporations have made more companies leery of supporting carbon-reduction projects.

“The perceptions of trust and feasibility associated with nature-based assets, both within the public and private sectors, have been adversely affected,” Austin noted. But he added that at this critical juncture:
“DMRV can have a significant impact to not only improve these markets but save them.”
It might be helpful to compare dMRV with traditional MRV, which aims to help prove that an activity — like planting trees or scrubbing smokestack emissions — has actually occurred. It is a prerequisite before a monetary value can be attached to the activity, and a necessity for carbon trading markets to work.
MRV has been “underpinning” sustainability reporting for years, Anna Lerner Nesbitt, CEO of the Climate Collective, told Cointelegraph. However, “it has a lot of weaknesses,” including a high reliance on subjective data, steep costs, lengthy timelines and a dependence on “international experts” — i.e., consultants.
Magazine: Recursive inscriptions: Bitcoin ‘supercomputer’ and BTC DeFi coming soon
According to Cambridge Centre’s Madhavapeddy, the inherent difficulty with quantifying nature-based projects “is that the conventional mechanisms for doing so — over the past decades — have been very manual and hard to compare across projects.”
Quantification mechanisms used for these assessments are far from being standardized. They include assessing “additionality” (i.e., what’s the net difference climatewise of a project?), permanence (how long will its effects last?), and leakage (did a negative externality, like cutting down a forest, just move somewhere else?).
DMRV, said Nesbitt, relies on emerging technologies and more granular data for “a fully digitized MRV protocol that not only collects digital data via Internet of Things, sensors and digital technologies but also processes and stores data on a fully digital and decentralized blockchain ledger.”
DMRV can also potentially reduce the workload of auditors and inspectors called upon to validate emissions-reduction projects, according to Daniel Voyce, chief technology officer of sustainability-focused solutions provider Tymlez, who wrote:
“With manual MRV recording each auditor or inspector might only be able to verify 150 projects each year due to chasing down the data they need and having to collate it all.”
Digitizing the process could reduce time and costs by 75%, he estimated.
Can blockchain help fix a “convoluted” process?
What role, if any, does blockchain play in all this? “I think if we are being honest, voluntary carbon markets — and regulated carbon markets — need blockchain for asset issuance and traceability,” Michael Kelly, co-founder and chief product officer at Open Forest Protocol — an open platform for scaling nature-based solutions — told Cointelegraph.
The current MRV process is “convoluted,” he said, with “no visibility into issuance schedules, no traceability, quite frequent double-spending, etc.” As a result, “people are hesitant to touch carbon credits.”
DMRV combined with blockchain could change things. “Once they can see everything about it [a project] — down to the upload of each tree in a sample plot for a 20-year time period — we will see new participants coming into the arena.”
Some incremental improvements in MRV — like digitizing submission forms — don’t really need blockchain tech, noted Nesbitt, but that might soon change with the addition of “features like smart contracts that allow for more inclusive or just asset pricing, baking in a reasonable compensation for local communities involved in carbon credit projects.”
However, there may be limits on how much blockchain tech alone can fix things. Blockchains can enable “transparency, security, automation and immutable records of data flows in an auditable fashion,” but that might not be enough, suggested Hyphen’s Austin, adding:
“DMRV can only be as good as the data and methodology used. If you take a flawed methodology and digitize it with blockchain, you now have an immutable and transparently flawed dMRV.”
Improving methodologies is crucial in Austin’s view. “Activity-based approaches work well in the case of combustion engines or industrial processes, which you can accurately measure and multiply by a factor,” he told Cointelegraph.
But these don’t really work on “nature-based solutions.” A forest in Brazil may sequester more carbon dioxide than an equally sized forest in Indonesia based on many variables, including drought, rainfall and humidity, for example.
“Nature is a breathing and living asset; therefore, methodologies need to measure the actual amount of CO2/CO2e [carbon dioxide/carbon dioxide equivalent] that is a sink or source instead of calculating a best guess,” said Austin.
Work is being done in this area, especially in the wake of the Verra controversy. “Researchers in this field are showing how the quality of ‘avoided deforestation’ carbon credits could be improved,” Julia Jones, professor in conservation science at Bangor University, told Cointelegraph. “However, there is, of course, some lag between new research and it getting into policy and practice.”
The Cambridge Center for Carbon Credits actually built a research prototype last year of what a carbon credits marketplace might look like on the Tezos blockchain. “Our first observation was that the blockchain really wasn’t the bottleneck here — all of that infrastructure works fine and has a solid technical roadmap for scaling,” Madhavapeddy told Cointelegraph. The barrier lay elsewhere.
“The blocker to any meaningful deployment came from the lack of supply of credible projects, since the quantification mechanisms” — i.e., additionality, permanence and leakage — “are only just maturing as satellite infrastructure and the associated algorithms are peer-reviewed and deployed.”

Kelly also cited a shortage of “quality carbon development projects and accessible credits,” especially in the nature-based asset subsector, as a significant obstacle for VCMs.
Projects like reforestation, afforestation, mangrove restoration and biodiversity conservation are now short of funding. This project shortfall leads to a low supply of credits, which becomes a sort of chicken-and-egg problem.
“The result of this system is that carbon credits remain a relatively illiquid, convoluted and difficult-to-scale system that disincentivizes stakeholders from financing, purchasing and trading the assets to participate in the market,” said Kelly.
“The biggest barrier right now is the collective credibility of the voluntary markets, and we hope that our work on the digitization and systematic design and publishing of analyses can help bridge that gap,” said Madhavapeddy.
A “perfect storm”?
What about claims, like those cited above, that dMRV technology has the potential to revolutionize the way the voluntary carbon market operates? Is that going too far?
Recent: Islamic finance and Web3 take stage at Istanbul Blockchain Week
“DMRV is at the center of strengthening data integrity, which in turn would improve process integrity,” said Nesbitt. “So yes, I think dMRV is vital to set up the voluntary carbon market for success. But saying it will revolutionize the market might be taking it a bit too far given the many dMRV improvements and applications already in implementation.”
Kelly sees two promising trends in the wake of the Guardian expose. Legacy incumbents like Verra and Gold Standard are now more intent on digitizing their processes and “becoming more transparent and trustworthy,” he said, while “stakeholders are more willing to try new solutions, or service providers, especially if they have higher standards for trust, visibility and quality.”
The result could be a “perfect storm for catalyzing a liquid voluntary carbon market — on-chain,” he added.
Cryptocurrency
Ethereum Foundation, Whales, and Hackers: What’s Driving the ETH Sell-Off?

TL;DR
- Whales, hackers, and the Ethereum Foundation wallets moved over $500M in ETH through large sales and withdrawals.
- Ethereum transfers rose to 4.6M ETH, nearing the monthly high of 5.2M recorded in July.
- Staking inflows hit 247,900 ETH, the highest in a month, locking more supply from trading.
Large Withdrawals and Whale Activity
Ethereum (ETH) has seen heavy movement from major wallets over the past few days. On-chain data from Lookonchain shows a newly created wallet pulled 17,591 ETH, worth $81.62 million, from Kraken in just two hours.
Over three days, two new wallets withdrew a combined 71,025 ETH, valued at $330 million, from the exchange.
One of these wallets, address 0x2A92, has withdrawn 53,434 ETH, worth $242.34 million, in two days. This includes a recent purchase of 30,069 ETH, valued at $138.46 million, during a market drop.
Major ETH Holders Offload Millions Amid Price Rally
In contrast, several separate entities have been disposing of some ETH holdings. A wallet tied to a hacker address 0x17E0 sold 4,958 ETH for $22.13 million at $4,463, securing a profit of $9.75 million. Earlier this year, the same address sold 12,282 ETH at $1,932 and later bought back part of the amount at higher prices.
A different whale sold 20,600 ETH for $96.55 million over the past two days, generating a profit of more than $26 million after holding the position for nine months.
Meanwhile, an Ethereum Foundation-linked wallet, 0xF39d, sold 6,194 ETH worth $28.36 million in the last three days at an average price of $4,578.
Recent sales from the same wallet included an additional 1,100 ETH and 1,695 ETH for over $12.7 million combined.
The #EthereumFoundation-linked wallet(0xF39d) sold another 1,300 $ETH($5.87M) at $4,518 ~11 hours ago.
Over the past 3 days, this wallet has sold a total of 6,194 $ETH($28.36M) at an average price of $4,578.https://t.co/4hfCWymHVG pic.twitter.com/ErUyEY8SJy
— Lookonchain (@lookonchain) August 15, 2025
Network Activity on the Rise
CryptoQuant data shows Ethereum’s total tokens transferred have been climbing since August 9. After ranging between 1 million and 3 million ETH through late July and early August, transfers have risen to 4.6 million ETH, approaching the monthly high of 5.2 million recorded in mid-July. This increase has occurred alongside a price rally from about $3,400 to $4,600.
Interestingly, staking inflows generally stayed between 20,000 and 80,000 ETH per day over the past month. On August 14, inflows jumped to 247,900 ETH, the highest in the period.
At the time, ETH was trading near $4,600. Large staking deposits reduce the amount of ETH available for immediate trading, as staked coins are locked for a set period.
In the meantime, ETH trades at $4,647 with a 24-hour volume of $68.25 billion, down 2% on the day but up 19% over the week.
Binance Free $600 (CryptoPotato Exclusive): Use this link to register a new account and receive $600 exclusive welcome offer on Binance (full details).
LIMITED OFFER for CryptoPotato readers at Bybit: Use this link to register and open a $500 FREE position on any coin!
Cryptocurrency
Massive DOGE Whale Activity Hints at $1 Breakout

TL;DR
- Whales bought two billion DOGE this week, lifting their combined holdings to 27.6 billion coins.
- A single 900M DOGE transfer worth $208M to Binance drew attention to large exchange movements.
- DOGE broke key resistance, with momentum building for a possible push toward the $1 price mark.
Price and Market Moves
Dogecoin (DOGE) traded at $0.23 at press time, slipping 4% over the past day but still showing a 2% gain for the week. Daily turnover came in at about $6.18 billion.
Meanwhile, the broader crypto market saw over $1 billion in liquidations. Hotter-than-expected US Producer Price Index data pushed traders to scale back expectations of a near-term Federal Reserve rate cut. DOGE had roughly 290,500 coins liquidated during the sell-off.
On the two-week chart, analyst Trader Tardigrade notes that DOGE has cleared a downward-sloping resistance line after completing what appears to be a “wave V” in an Elliott Wave sequence. Similar setups in the past, where prolonged declines stayed within falling channels before breaking higher, have been followed by sharp rallies.
$Doge/2-week#Dogecoin is gaining strong momentum to surge above $1 pic.twitter.com/TuSEKr19nv
— Trader Tardigrade (@TATrader_Alan) August 15, 2025
Momentum gauges are also turning up. The Stochastic RSI, which had dropped into oversold territory, is now heading higher. Previous reversals from this zone have coincided with sustained upward moves. The current formation points to a possible run that could carry DOGE past the $1 mark.
Heavy Whale Buying and Large Transfers
As reported by CryptoPotato, blockchain data shows large investors have added two billion DOGE in the past week, spending just under $500 million. That brings their holdings to about 27.6 billion coins, or 18% of the supply. The buying streak has prompted speculation within the community.
Recently, Whale Alert flagged a 900 million DOGE transfer worth about $208 million into Binance. The tracking indicates that it originated from a wallet connected to the exchange, likely as an internal activity. The address involved holds 2.88 billion DOGE, one of the largest balances on the network.
Ali Martinez also reports that transactions above $1 million reached a one-month high, with activity building since early August and peaking as DOGE traded at $0.25.
Whales are back! Dogecoin $DOGE activity at a 1-month high. pic.twitter.com/C83Pv68mCt
— Ali (@ali_charts) August 14, 2025
Sentiment Building
Analyst Gordon described the current setup as “a nice bit of consolidation” before a potential breakout, adding,
“This will be one of the first coins normies FLOCK to & the pump will be MASSIVE.”
With whale accumulation rising, high-value transfers increasing, and a bullish technical pattern in play, DOGE is positioned for a potential push toward $1 if momentum holds.
Binance Free $600 (CryptoPotato Exclusive): Use this link to register a new account and receive $600 exclusive welcome offer on Binance (full details).
LIMITED OFFER for CryptoPotato readers at Bybit: Use this link to register and open a $500 FREE position on any coin!
Cryptocurrency
Ripple Price Analysis: XRP at Risk as Key Support Levels Could Trigger Sharp Drop
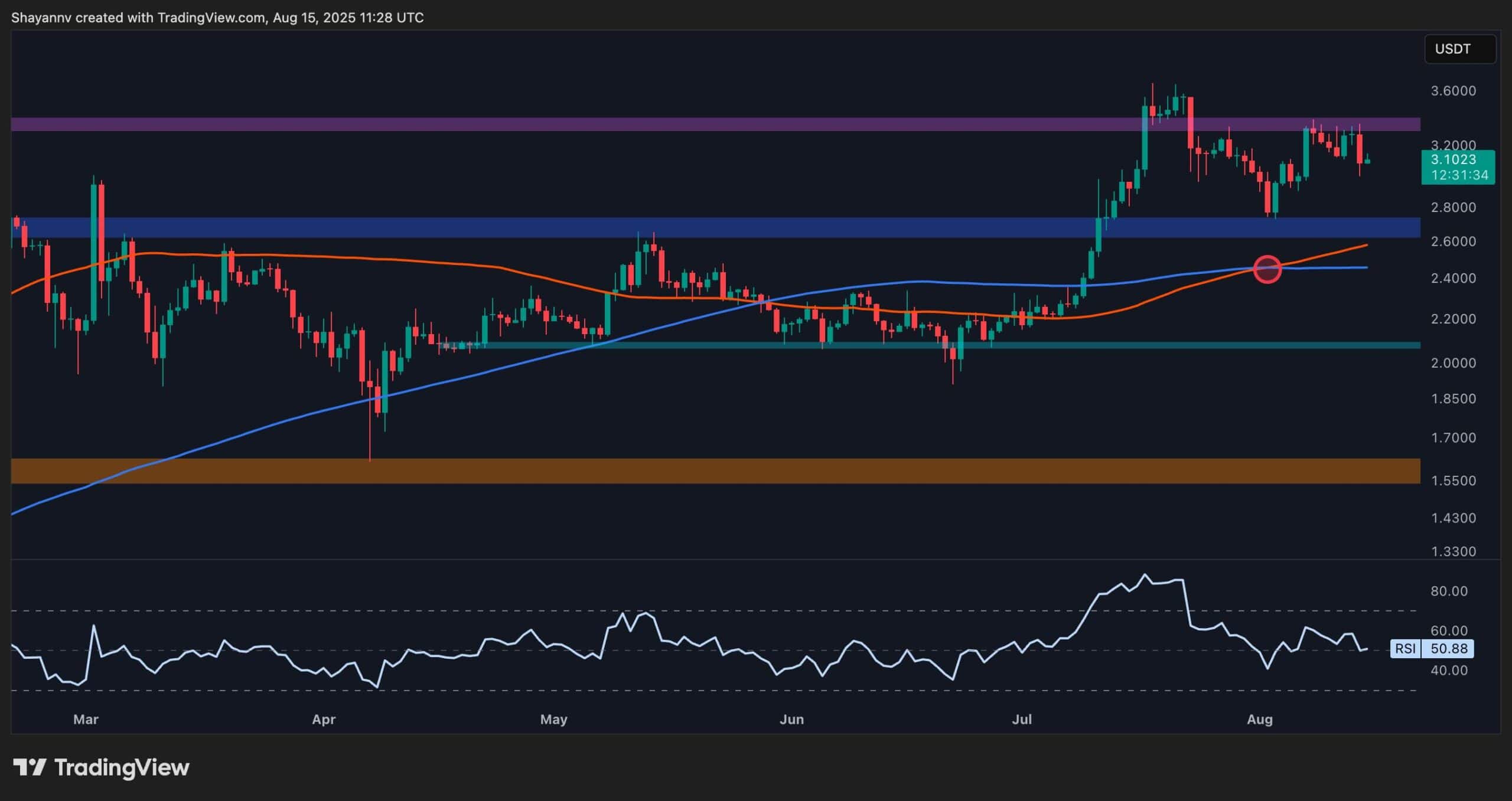
XRP has recently entered a consolidation phase after a strong rally earlier this summer, with the price action now hovering around key resistance levels on both its USDT and BTC pairs. Yet, while momentum has slowed, the charts still indicate a generally bullish structure, with multiple key support levels remaining firmly in place.
Technical Analysis
By ShayanMarkets
The USDT Pair
On the XRP/USDT daily chart, the price is currently trading near the $3.10 mark, facing a strong resistance zone around $3.40. This follows a breakout above the $2.70 range in July, which has now flipped into a support area.
Both the 100-day and 200-day moving averages are also trending upward and recently formed a bullish crossover around $2.45, reinforcing the medium-term bullish sentiment. If the $3.40 resistance breaks, a push toward the critical $4.00 range becomes likely.
However, the RSI hovering near the neutral 50 level suggests a lack of strong momentum for now, meaning a short-term pullback into the $2.80 support zone is still possible.
This zone will be key for maintaining the bullish structure. Losing it could open the door for a deeper correction toward the 200-day moving average located around the $2.40 mark. Yet, as long as the price stays above the moving averages, the broader trend remains bullish.
The BTC Pair
Looking at the XRP/BTC chart, the pair has recently pulled back after hitting the 3,000 SAT resistance, with the price currently around 2,600 SAT.
This follows a clean breakout above the long-term descending channel and a successful retest of its upper boundary, which coincided with the 200-day moving average and the 2,400 SAT support zone. This confluence remains a key bullish technical factor, as holding above it could attract renewed buying pressure.
That said, RSI levels around 48 show that momentum has cooled after the sharp July rally, meaning XRP may continue ranging between 2,400 SAT and 3,000 SAT in the near term. A decisive close above 3,000 SAT would likely open the path to the 3,400 SAT zone, while losing 2,400 SAT could shift the bias back toward 2,000 SAT support. For now, the structure still favors the bulls as long as higher lows remain intact.
Binance Free $600 (CryptoPotato Exclusive): Use this link to register a new account and receive $600 exclusive welcome offer on Binance (full details).
LIMITED OFFER for CryptoPotato readers at Bybit: Use this link to register and open a $500 FREE position on any coin!
Disclaimer: Information found on CryptoPotato is those of writers quoted. It does not represent the opinions of CryptoPotato on whether to buy, sell, or hold any investments. You are advised to conduct your own research before making any investment decisions. Use provided information at your own risk. See Disclaimer for more information.
Cryptocurrency charts by TradingView.

 Forex3 years ago
Forex3 years agoForex Today: the dollar is gaining strength amid gloomy sentiment at the start of the Fed’s week

 Forex3 years ago
Forex3 years agoUnbiased review of Pocket Option broker

 Forex3 years ago
Forex3 years agoDollar to pound sterling exchange rate today: Pound plummeted to its lowest since 1985

 Forex3 years ago
Forex3 years agoHow is the Australian dollar doing today?

 Cryptocurrency3 years ago
Cryptocurrency3 years agoWhat happened in the crypto market – current events today

 World3 years ago
World3 years agoWhy are modern video games an art form?

 Commodities3 years ago
Commodities3 years agoCopper continues to fall in price on expectations of lower demand in China

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoCrude oil tankers double in price due to EU anti-Russian sanctions























