Forex
Explainer-What would Japanese intervention to boost a weak yen look like?

By Leika Kihara
TOKYO (Reuters) -Japanese authorities are facing renewed pressure to combat a sustained depreciation in the yen, as traders drive down the currency on expectations that any further interest rate hikes by the central bank will be slow in forthcoming.
Below are details on how yen-buying intervention works:
LAST CONFIRMED YEN-BUYING INTERVENTION?
Japan bought yen in September 2022, its first foray in the market to boost its currency since 1998, after a Bank of Japan (BOJ) decision to maintain its ultra-loose monetary policy drove the yen as low as 145 per dollar. It intervened again in October after the yen plunged to a 32-year low of 151.94.
WHY STEP IN?
Yen-buying intervention is rare. Far more often the Ministry of Finance has sold yen to prevent its rise from hurting the export-reliant economy by making Japanese goods less competitive overseas.
But yen weakness is now seen as problematic, with Japanese firms having shifted production overseas and the economy heavily reliant on imports for goods ranging from fuel and raw materials to machinery parts.
WHAT HAPPENS FIRST?
When Japanese authorities escalate their verbal warnings to say they “stand ready to act decisively” against speculative moves, that is a sign intervention may be imminent.
Rate checking by the BOJ – when central bank officials call dealers and ask for buying or selling rates for the yen – is seen by traders as a possible precursor to intervention.
WHAT HAPPENED SO FAR?
Finance Minister Shunichi Suzuki told reporters on March 27 that authorities could take “decisive steps” against yen weakness – language he hasn’t used since the 2022 intervention.
remove ads
.
Hours later, Japanese authorities held an emergency meeting to discuss the weak yen. The meeting is usually held as a symbolic gesture to markets that authorities are concerned about rapid currency moves.
After the warnings failed to arrest the yen’s fall, South Korea and Japan won acknowledgement from the United States over their “serious concerns” about their currencies’ declines in a trilateral meeting held in Washington last week.
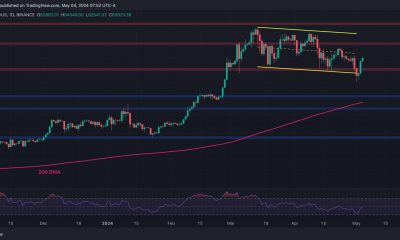
The market impact of the agreement did not last long. The dollar continued its ascent and notched a 34-year high of 155.74 yen on Thursday, driving past the 155 level seen as authorities’ line in the sand for intervention.
NEXT LINE IN THE SAND?
Authorities say they look at the speed of yen falls, rather than levels, and whether the moves are driven by speculators, to determine whether to step into the currency market.
While the dollar has moved above the psychologically important 155 level, the recent rise has been gradual and driven mostly by U.S.-Japanese interest rate differentials. That may make it hard for Japan to argue that recent yen falls are out of line with fundamentals and warrant intervention.
Some market players bet Japanese authorities’ next line in the sand could be 160. Ruling party executive Takao Ochi told Reuters the yen’s slide towards 160 or 170 to the dollar could prod policymakers to act.
WHAT’S THE TRIGGER?
The decision is highly political. When public anger over the weak yen and a subsequent rise in the cost of living is high, that puts pressure on the administration to respond. This was the case when Tokyo intervened in 2022.
remove ads
.
Prime Minister Fumio Kishida may feel the need to prevent further yen falls from pushing up the cost of living with his approval ratings faltering ahead of a ruling party leadership race in September.
But the decision would not be easy. Intervention is costly and could easily fail, given that even a large burst of yen buying would pale next to the $7.5 trillion that change hands daily in the foreign exchange market.
HOW WOULD IT WORK?
When Japan intervenes to stem yen rises, the Ministry of Finance issues short-term bills, raising yen it then sells to weaken the Japanese currency.
To support the yen, however, the authorities must tap Japan’s foreign reserves for dollars to sell for yen.
In either case, the finance minister issues the order to intervene and the BOJ executes the order as the ministry’s agent.
CHALLENGES?
Japanese authorities consider it important to seek the support of Group of Seven partners, notably the United States if the intervention involves the dollar.
Washington gave tacit approval when Japan intervened in 2022, reflecting recent close bilateral relations.
Finance Minister Suzuki said last week’s meeting with his U.S. and South Korean counterparts laid the groundwork to act against excessive yen moves, a sign Tokyo saw the meeting as informal consent by Washington to intervene as needed.
A looming U.S. presidential election may complicate Japan’s decision on whether and when to intervene.
In a social media post on Tuesday, Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump decried the yen’s historic slide against the dollar, calling it a “total disaster” for the United States.
remove ads
.
There is no guarantee intervention will effectively shift the weak-yen tide, which is driven largely by expectations of prolonged low interest rates in Japan. BOJ Governor Kazuo Ueda has dropped hints of another rate hike but stressed that the bank will tread cautiously given Japan’s fragile economy.
Forex
Yen higher after suspected intervention

By Karen Brettell
NEW YORK (Reuters) – The yen gained on Thursday, following a sudden rally late on Wednesday that traders and analysts attributed to intervention by Japanese authorities, while the dollar was broadly lower before key jobs data on Friday.
The sharp move in the yen on Wednesday came in a quiet period for markets after Wall Street had closed, and hours after the U.S. Federal Reserve had wrapped up its policy meeting.
Fed Chair Jerome Powell confirmed the central bank’s expectation to cut rates, but acknowledged such a move would come later than expected due to stubbornly high inflation.
The dollar eased, however, due to the Fed not adopting a more hawkish tone that included the potential for further rate hikes.
The timing of the intervention was “pragmatic,” as “volumes were light, liquidity was thin, and it’s easier to make an impact at that time,” said Brad Bechtel, global head of FX at Jefferies in New York.
The dollar was last down 0.9% at 153.09 yen..
Japan’s vice finance minister for international affairs, Masato Kanda, who oversees currency policy at the Ministry of Finance, told Reuters he had no comment on whether Japan had intervened in the market.
Wednesday’s volatility came after a similar move on Monday, which was also during a time of light trading.
“Clearly they want to make as much as an impact and do it as efficiently as possible,” said Bechtel.
The Bank of Japan’s official data indicated Japan may have spent 3.66 trillion yen ($23.59 billion) on Wednesday and 5.5 trillion yen ($35.06 billion) supporting the currency on Monday to pull it back from new 34-year lows.
remove ads
.
While the supposed interventions may buy Japan some time, the trend is likely to remain negative for the Japanese currency until the U.S. economy slows and as long as the Bank of Japan disappoints traders on how far it is willing to raise rates.
The dollar remains up more than 10% against the yen this year, as traders push back expectations on the timing of a first Fed rate cut, while the BOJ has signaled it will go slow with further policy tightening after raising rates in March for the first time since 2007.
The next major U.S. economic focus that could drive further moves in dollar/yen will be Friday’s jobs report for April, which is expected to show that employers added 243,000 jobs during the month.
“A lot hinges on tomorrow’s jobs report,” said Marc Chandler, chief market strategist at Bannockburn Global Forex in New York.
A weaker number would give Japanese authorities relief, and likely pull Treasury yields and the dollar lower. A strong report, however, could send yields and the greenback higher and increase the risk of further interventions.
If 10-year Treasury yields approach the 5% region, “I’d say the dollar/yen is going to come under more pressure,” said Chandler. “It’s all about what happens with U.S. rates – we’re sort of the big moving piece.”
Benchmark 10-year Treasury yields were last at 4.57%.
Data on Thursday showed that the number of Americans filing new claims for unemployment benefits held steady at a low level last week.
remove ads
.
The fell 0.38% to 105.31, while the euro gained 0.17% to $1.0728.
The dollar weakened 0.59% to 0.91 Swiss francs after Swiss annual inflation in April accelerated faster than expected.
In cryptocurrencies, bitcoin gained 3.56% to $59,319.
Forex
Asia FX on guard before payrolls data, yen rebounds amid likely intervention

Investing.com– Most Asian currencies rose slightly on Friday, capitalizing on a drop in the dollar as markets hunkered down before key U.S. payrolls data that is likely to factor into interest rates.
The dollar was also pressured by a rebound in the Japanese yen, which pulled further away from 34-year lows amid what appeared to be government intervention in currency markets.
Weakness in the dollar offered some breathing room to regional currencies, although they were still nursing steep losses on the prospect of U.S. interest rates remaining high for longer.
Japanese yen firms amid likely intervention, USDJPY at 3-week low
The Japanese yen saw extended gains on Friday, with the pair- which moves inversely to strength in the yen- falling 0.4% to 153.02. The pair briefly hit a three-week low of 152.9.
The USDJPY pair was set to lose about 3.4% this week as it tumbled from 34-year highs. Traders and analysts attributed the drop largely to currency market intervention by the Japanese government.
The USDJPY pair had surged to 160 earlier this week. Traders said this level was the new line in the sand for currency market intervention.
Domestic Japanese markets were closed on Friday. But the lower volumes also aided the yen.
Still, the factors that had spurred recent yen weakness remained in play, chiefly the prospect of high-for-longer U.S. interest rates.
Broader Asian currencies rose slightly, capitalizing on an overnight drop in the dollar. The Australian dollar’s pair rose 0.2%, as markets positioned for potentially hawkish signals from the next week. Hotter-than-expected Australian inflation readings saw markets largely price out expectations of any rate cuts by the RBA in 2024, offering the Aussie some strength.
remove ads
.
Trading volumes in Asia remained muted on account of market holidays in Japan and China.
The South Korean won’s pair fell 0.3%, while the Singapore dollar’s pair fell 0.1%.
The Indian rupee’s pair fell slightly, and was trading well below record highs hit in April.
Dollar steadies from overnight losses, nonfarm payrolls awaited
The and steadied in Asian trade after tumbling in overnight trade, as pressure from the yen and expectations of no more interest rate hikes by the Federal Reserve dented the greenback.
Focus was now squarely on data for April, which is due later in the day. The reading has consistently beaten estimates for the past five months, with any signs of persistent labor market strength giving the Fed more headroom to keep rates high for longer.
The Fed signaled earlier this week that it had no plans to cut rates in the near-term, especially in the face of sticky inflation.
Forex
Japanese yen rises, USDJPY hits 3-week low on suspected intervention

Investing.com– The Japanese yen firmed on Friday, with the USDJPY pair hitting a three-week low after sharp declines through this week that traders largely attributed to government intervention.
The pair, which gauges the amount of yen required to buy one dollar, was trading down 0.2% at 153.34 yen. It had fallen as low as 152.9 on Thursday, reaching its weakest level since mid-April.
The USDJPY pair fell sharply through this week amid increasing evidence that the Japanese government had intervened in markets on at least three separate instances- on Monday, Wednesday and Thursday.
The suspected intervention came after the USDJPY pair surged to 160 at the beginning of the week, which traders said was the new line in the sand for the yen. The Japanese currency started the week at its weakest level since 1990.
The factors that had pressured the yen in the lead-up to this week still remained in play. Recent comments from the U.S. Federal Reserve reinforced expectations that interest rates will remain high for longer.
A widening gap between U.S. and Japanese rates was a key point of pressure on the yen, with a historic rate hike by the Bank of Japan in March doing little to alleviate this pressure.
The BOJ also offered middling signals on future rate hikes during a late-April meeting, which triggered the yen’s recent bout of losses.
While Japanese government officials did not directly confirm this week’s intervention, Reuters estimated that Japan may have spent between 3.66 trillion yen and 5.5 trillion yen ($23.59 billion- $35.06 billion) when intervening in markets on Monday, based on BOJ data.
remove ads
.

 Forex2 years ago
Forex2 years agoForex Today: the dollar is gaining strength amid gloomy sentiment at the start of the Fed’s week

 Forex2 years ago
Forex2 years agoHow is the Australian dollar doing today?

 Forex1 year ago
Forex1 year agoUnbiased review of Pocket Option broker

 Forex2 years ago
Forex2 years agoDollar to pound sterling exchange rate today: Pound plummeted to its lowest since 1985

 Cryptocurrency2 years ago
Cryptocurrency2 years agoWhat happened in the crypto market – current events today

 World2 years ago
World2 years agoWhy are modern video games an art form?

 Stock Markets2 years ago
Stock Markets2 years agoMorgan Stanley: bear market rally to continue

 Economy2 years ago
Economy2 years agoCrude oil tankers double in price due to EU anti-Russian sanctions