Stock Markets
World’s largest cruise ship sets sail, bringing concerns about methane emissions


© Reuters
By Doyinsola Oladipo
NEW YORK (Reuters) – The world’s largest cruise ship is set for its maiden voyage on Saturday, but environmental groups are concerned that the liquefied natural gas-powered vessel – and other giant cruise liners to follow – will leak harmful methane into the atmosphere.
Royal Caribbean (NYSE:) International’s Icon (NASDAQ:) of the Seas sets sail from Miami with capacity for 8,000 passengers across 20 decks, taking advantage of the surging popularity of cruises.
The ship is built to run on liquefied (LNG), which burns more cleanly than traditional marine fuel but poses greater risks for methane emissions. Environmental groups say methane leakage from the ship’s engines is an unacceptable risk to the climate because of its short-term harmful effects.
“It’s a step in the wrong direction,” said Bryan Comer, director of the Marine Program at the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT), an environmental policy think tank.
“We would estimate that using LNG as a marine fuel emits over 120% more life-cycle greenhouse gas emissions than marine gas oil,” he said.
In terms of warming effects, methane is 80 times worse over 20 years than carbon dioxide, making cutting those emissions key to holding down global temperature warming.
Cruise ships like Icon of the Seas use low-pressure, dual-fuel engines that leak methane into the atmosphere during the combustion process, known as “methane slip,” according to industry experts. There are two other engines used on bulk carriers or container ships that emit less methane but they are too tall to fit in a cruise ship.
Royal Caribbean says its new ship is 24% more efficient when it comes to carbon emissions than required by global shipping regulator the International Maritime Organization (IMO).
LNG emits fewer greenhouse gases than very low sulfur fuel oil (VLSFO) that powers most of the global shipping fleet, said Steve Esau, chief operating officer of Sea-LNG, a industry advocacy organization.
Cruise engines convert natural gas into power in a cylinder, where it is “important to make sure that all the natural gas is converted to energy,” said Juha Kytölä, director of R&D and Engineering at Wärtsilä, which developed the cruise ship’s engines.
What is not converted can escape during the combustion process into the atmosphere, he said, adding that Wärtsilä’s natural gas engine technology emits 90% less methane than it did 20 to 30 years ago.
Cruise ship engines have an estimated methane slip of 6.4% on average, according to 2024 research funded by the ICCT and other partners. The IMO assumes methane slip at 3.5%.
“Methane is coming under more scrutiny,” said Anna Barford, Canada shipping campaigner at Stand Earth, a nonprofit organization, noting that the IMO last summer said its efforts to cut greenhouse gases includes addressing methane emissions.
Of the 54 ships on order from January 2024 to December 2028, 63% are expected to be powered by LNG, according to the Cruise Line International Association. Currently, about 6% of the 300 cruise ships sailing are fueled by LNG.
Newer cruise ships are being designed to run on traditional marine gas oil, LNG or alternatives like bio-LNG that only account for a fraction of U.S. fuel consumption.
Royal Caribbean will use different fuels as the market evolves, said Nick Rose, the company’s vice president of environmental, social, and governance.
“LNG is one piece of our actual strategy,” he said.
Stock Markets
Analysis-Warren Buffett’s PacifiCorp utility singed by wildfires

By Jonathan Stempel
OMAHA, Nebraska (Reuters) – Two years ago, Warren Buffett branded Berkshire Hathaway (NYSE:)’s energy business one of his conglomerate’s four “giants.” Now he fears its business model may be broken.
Berkshire Hathaway Energy’s PacifiCorp unit faces billions of dollars in potential liabilities from wildfires that have scorched hundreds of thousands of acres in southern Oregon and northern California.
Costs could rise as more fires break out, and from efforts to prevent them. Climate change, reflected in drier and hotter weather and more combustible vegetation, adds to the risks.
“I did not anticipate or even consider the adverse developments in regulatory returns,” Buffett wrote in his annual shareholder letter in February. “I made a costly mistake in not doing so.”
What remains unclear is the extent PacifiCorp’s problems drag on the conglomerate’s overall results, with Berkshire’s deep balance sheet and dozens of other operations being unable to totally counteract.
Buffett, 93, and his designated successor Greg Abel, 61, may face shareholder questions at Berkshire’s May 4 annual meeting in Omaha, Nebraska, about their concerns for the energy company.
“Wildfires make (the utilities) fire insurance companies on top of being utilities,” said Steven Check, who oversees $1.9 billion at Check Capital management, including $600 million in Berkshire stock and options. “It is a material change. Warren Buffett did not see this coming at all.”
ESCALATING CLAIMS
Berkshire Hathaway Energy serves about 5.3 million electric and gas customers through PacifiCorp, MidAmerican Energy and NV Energy in 11 western and Midwestern states, and millions more in England and Alberta, Canada.
remove ads
.
It owns 36,400 miles (58,580 km) of electric transmission lines, and operates 21,000 miles of pipelines.
For many years, Berkshire Hathaway Energy – which is 92% owned by Berkshire Hathaway – had been a steady earnings engine for its parent, typically generating 10% to 12% of overall operating profit.
That fell to just 6% in 2023, as the business’s profit slid 40% to $2.33 billion.
PacifiCorp was a big reason. Jurors have found the Portland, Oregon-based utility liable in several verdicts over wildfires from 2020, blaming losses on its power lines. PacifiCorp has denied negligence.
But it ended 2023 with $2.4 billion of projected wildfire losses, and has said losses could grow to $8 billion.
This week, a group of 1,000 fire victims said PacifiCorp should pay them $30 billion.
One result: PacifiCorp will pay no dividends to Berkshire Hathaway Energy for several years, which could affect the parent’s ability to fund operations.
“It’s key for utilities to recover costs and maintain a strong financial profile so they can ensure reliability for customers,” said Travis Miller, a Morningstar stock analyst.
Utilities can reduce the risk of wildfires by insulating wires to reduce the threat of sparks, trimming or cutting down trees that could contact power equipment, burying transmission lines underground, and temporarily shutting off power.
But mitigation can be expensive, and Buffett pledged that Berkshire “will not knowingly throw good money after bad.”
Toby Shea, senior credit officer at Moody’s (NYSE:) Investors Service, explained: “He’s saying, look, if we basically have to pay out billions and billions of dollars every time there is a big fire, this is not a workable model.”
remove ads
.
BLAME THE LAWYERS This is not the first time Berkshire has encountered big headwinds in a major business.
Berkshire spent years cleaning up poor underwriting at General Re after paying $16 billion for the reinsurer in 1998.
It also overpaid for Precision Castparts, which cost $32.1 billion in 2016, only to see its aircraft parts business collapse during the pandemic. Litigation involving PacifiCorp could drag out for years, and the ultimate cost and timing of payouts are uncertain.
In his shareholder letter, Buffett warned that a “confiscatory resolution” might befall PacifiCorp, but that Berkshire and Berkshire Hathaway Energy were structured to survive it.
Though analysts do not foresee a bankruptcy, Berkshire could decide it might not be worth investing in generating and transmission assets if it were forced to foot several years of big legal bills.
“Our assumption is that if damages at PacifiCorp become unsustainable long term, the company’s support toward PacifiCorp could be limited,” S&P Global analyst Sloan Millman said.
Berkshire Hathaway Energy declined to comment for this article.
PacifiCorp said the $30 billion claim shows the need for legal reform, with its ability to serve customers “threatened by excessive wildfire damages pursued by plaintiffs’ attorneys who have a substantial financial stake in these outcomes.”
Some states are addressing utilities’ risk of bankruptcy from wildfires.
In 2019, California lawmakers created a multibillion-dollar wildfire fund that utilities could tap to pay for damages caused by their equipment.
And in March 2024, Utah lawmakers allowed large utilities to collect surcharges from customers to establish wildfire funds, and capped liability on some claims.
remove ads
.
PacifiCorp could benefit if Oregon took similar steps. For now, Berkshire’s size offers protection from big losses.
Paul Lountzis, president of Lountzis Asset Management in Wyomissing, Pennsylvania, which invests 11% of its assets in Berkshire stock, said diversification “really, really helps. It’s not like Berkshire is one singular utility.”
Stock Markets
Bitcoin vs Gold: Peter Schiff and Anthony Scaramucci Clash in Epic Debate

U.Today – In a heated live debate organized by ZeroHedge and presented on YouTube, billionaire investor Anthony Scaramucci of SkyBridge Capital sparred with top analyst Peter Schiff over whether (BTC) or gold serves as a better inflation hedge.
They were joined by the CEO of ShapeSchift Erik Voorhees and Nouriel Roubini, a professor of economics at NYU.
BTC as digital gold
Bitcoin proponents are attempting to reposition it as a digital version of gold, Schiff said. Still, in his view, it falls short of gold’s intrinsic value derived from its physical properties.
“Bitcoin is no more digital gold than an image of a hamburger is digital food,” Schiff noted.
He emphasized gold’s tangible utility in industries like jewelry and electronics, contrasting it with Bitcoin, which he believes lacks practical uses and utility.
Regarding gold’s enduring value, Schiff asserted that it retains its intrinsic properties over time, serving as a genuine store of value. He also argued that the perceived value of Bitcoin is merely based on speculative demand and does not reflect any inherent usefulness or practical applications.
BTC as asset
He emphasized that Bitcoin, like gold, has a deflationary aspect due to its fixed supply. Scaramucci views Bitcoin as “digital gold,” noting its portability compared to physical gold.
He also pointed that Bitcoin is following an adoption curve that will impact its value over decades, likening it to the trajectory of tech stocks that became standard over time and contributed to the S&P 500 index.
remove ads
.
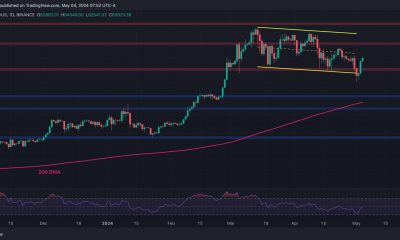
BTC breaks $63K
Source: CoinMarketCapThis surge followed a cooler-than-expected U.S. April jobs report, which alleviated concerns about potential increases in interest rates.
Stock Markets
Death toll from rains in southern Brazil climbs to 57, some 70 still missing
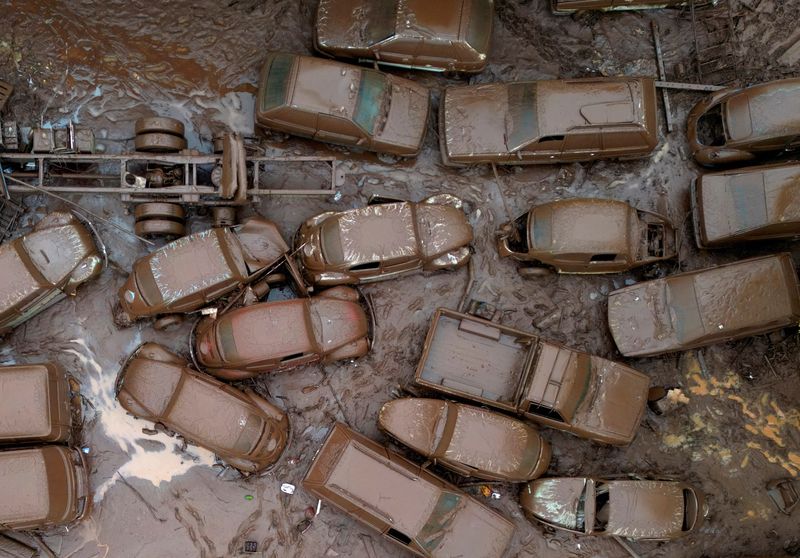

SAO PAULO (Reuters) -The death toll from rains in Brazil’s southernmost state of Rio Grande do Sul rose to 57, local authorities said on Saturday afternoon, while dozens still have not been accounted for.
Rio Grande do Sul’s civil defense authority said 67 people were still missing and more than 32,000 had been displaced as storms have affected nearly two thirds of the 497 cities in the state, which borders Uruguay and Argentina.
Floods destroyed roads and bridges in several regions of the state. The storm also triggered landslides and the partial collapse of a dam at a small hydroelectric power plant. A second dam in the city of Bento Goncalves is also at risk of collapsing, authorities said.
In Porto Alegre, the capital of Rio Grande do Sul, the Guaiba lake broke its banks, flooding streets.
Porto Alegre’s international airport has suspended all flights for an indefinite period.
Rains are expected in the northern and northeastern regions of the state in the next 36 hours, but the volume of precipitation has been declining, and should be well below the peak seen earlier in the week, according to the state meteorology authority.
Still, “rivers water levels should stay high for some days”, Governor Eduardo Leite said on Saturday in a live video on his social media, adding it is difficult to determine for how long.
Rio Grande do Sul is at a geographical meeting point between tropical and polar atmospheres, which has created a weather pattern with periods of intense rains and others of drought.
remove ads
.
Local scientists believe the pattern has been intensifying due to climate change.
Heavy rains had already hit Rio Grande do Sul last September, as an extratropical cyclone caused floods that killed more than 50 people.
That came after more than two years of a persistent drought due to the La Nina phenomenon, with only scarce showers.

 Forex2 years ago
Forex2 years agoForex Today: the dollar is gaining strength amid gloomy sentiment at the start of the Fed’s week

 Forex2 years ago
Forex2 years agoHow is the Australian dollar doing today?

 Forex1 year ago
Forex1 year agoUnbiased review of Pocket Option broker

 Forex2 years ago
Forex2 years agoDollar to pound sterling exchange rate today: Pound plummeted to its lowest since 1985

 Cryptocurrency2 years ago
Cryptocurrency2 years agoWhat happened in the crypto market – current events today

 World2 years ago
World2 years agoWhy are modern video games an art form?

 Stock Markets2 years ago
Stock Markets2 years agoMorgan Stanley: bear market rally to continue

 Economy2 years ago
Economy2 years agoCrude oil tankers double in price due to EU anti-Russian sanctions